Reclaim Your Weekends With Rapid Culture Media in Food Microbiology
Ensuring food safety requires accurate and timely microbial testing, yet extended incubation periods often push results into the weekend, disrupting workflows.
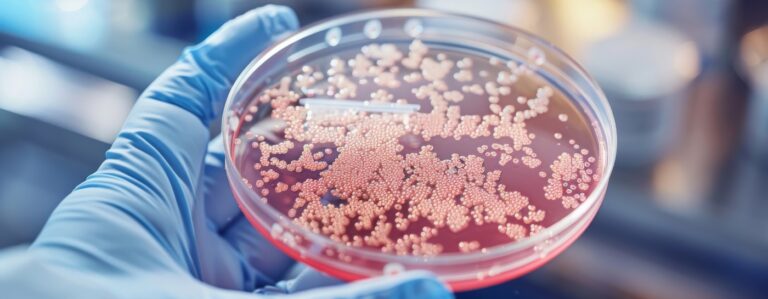
Ensuring food safety requires accurate and timely microbial testing, yet extended incubation periods often push results into the weekend, disrupting workflows.

In the highly regulated pharmaceutical industry, ensuring the safety and longevity of non-sterile aqueous products is paramount. Antimicrobial preservatives are crucial in preventing microbial contamination, which can compromise product integrity and patient safety.

High Pressure Processing (HPP) uses elevated pressure to inactivate microorganisms and enzymes in foods. It causes microbial inactivation by altering the cell membrane permeability and inhibiting enzyme activity, protein denaturation, and ribosome destruction. HPP targets cell membranes and walls and can inactivate both vegetative cells and spores too.

Eating a diet rich in fruits and vegetables is often touted as a healthy choice, but it is important to remember that food safety is just as important as nutrition. We need to be aware of the safety of the food we consume, and this includes the food we purchase from the supermarket.

When it comes to grocery shopping, food safety is a top priority for consumers as we all want to make sure that the food we bring home is safe to eat. Therefore, consumers need to be aware of the prevalence of food pathogens in foods when purchasing from supermarkets, understand the potential risks, and how to minimize them.

Acidulants such as acetic, adipic, citric, fumaric, lactic, malic, phosphoric, tartaric acids, and glucono-delta-lactone are commonly used as food additives in processed foods and beverages. They are used for leavening functions in baked goods, control gel formation, and maintaining the viscosity of confections and gelatin desserts.

When it comes to food safety and quality, there are two critical measurements that all food manufacturers must be concerned with: moisture content and water activity.

In the field of food safety, hurdle technology is a method of ensuring the safety of foods by eliminating or controlling the growth of pathogens. It is a gentle and effective preservation technique used for the inactivation of microorganisms to make food safe for public consumption and extend their shelf life.

Each time we purchase food in convenience stores such as bread, milk, yogurt, and other ready-to-eat food, we know that these products have a limited shelf life. Food is perishable by nature and numerous changes take place in food during processing and storage.

Let us first understand what a sampling plan is. Often, this is an approach used by an auditor or researcher to study a batch of products or a segment of the materials. The plan will contain a detailed outline of measurements taken of the samples at what times, on which material, in what manner, and by whom.
Delivering Growth – in Asia and Beyond.
© DKSH International Ltd.
Please enter your details here: