
Chemical testing of pharmaceutical products includes the identification of molecules and compounds, testing of stability, and the identification of chemical impurities per pharmacopeia specifications.
Applications of Light Microscopy

Testing of incoming raw materials is an essential step in the manufacturing of pharmaceutical products, as to guarantee safety and efficacy of a finished dosage form, which is largely dependent on the purity and quality of the bulk active drug substance and excipient. It is key to have a high-throughput method for analyzing the sample in a loading bay or warehouse, while also preventing sample exposure to contaminants.
Application
- USP <1858> Raman Spectroscopy – Theory and Practice
- USP <197> Spectrophotometric Identification Tests
- USP <621> Chromatography
- USP <856> Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
- USP <858> Raman Spectroscopy
- USP <1119> Near-Infrared Spectroscopy
Related products

Metrohm NIRS XDS MasterLab Analyzer
Rapid, nondestructive analyses of tablets, capsules and other solid-state dosage forms
To ensure the safety and quality before releasing the drug to the market, pharmaceutical companies must evaluate the interactions between packaging material and formulation. Extractables and leachables studies are key indicators for product quality during drug development and final batch release. The testing process assesses whether the drug products could have been exposed to harmful leachable contaminants.
Application
- USP <1664> Assessment of Drug Product Leachables Associated with Pharmaceutical Packaging/Delivery systems.
- USP <621> Chromatography
- USP <1663> Assessment of Extractables Associated with Pharmaceutical Packaging/Delivery Systems

Organic impurities can arise in APIs or drug product formulations during the manufacturing process or during the storage of drug substances. This includes volatile or nonvolatile compounds from starting materials, intermediates, unintended byproducts and degradation products. Organic impurities most often result in undesired biological activity or toxicity.
Application
- USP <621> Chromatography
- USP <197> Spectrophotometric Identification Tests
- USP <476> Organic Impurities in Drug Substances and Drug Products

Trace amounts of residual solvents can be found in pharmaceutical products used during drug production. Strict regulations on monitoring the presence of residual solvents is required as even the most trace amount can impact drug safety and efficacy.
Application
- USP <621> Chromatography
- USP <467> Residual Solvents

In accordance with Pharmacopoeias, for reasons of patient safety, the heavy metals in pharmaceutical finished products and raw materials must not exceed specified limit values. Heavy metals can be introduced into the product via catalysts, synthesis reagents and through contaminants in the manufacturing process.
Application
- USP <671> Containers – Performance Testing
- USP <232> Elemental Impurities – Limits
- USP <233> Elemental Impurities – Procedures
- USP <661> Plastic Packaging Systems and Their Materials of Construction

Stability testing provides evidence on how the quality of a drug substance or product varies with time. Testing is performed under the influence of environmental factors such as temperature, humidity and light. The studies are designed to include testing of attributes susceptible to change during storage and are likely to influence quality, safety and efficacy. Stability conditions are governed by the International Conference on Harmonization (ICH).
Application
- USP <1079> Good Storage and Shipping Practices
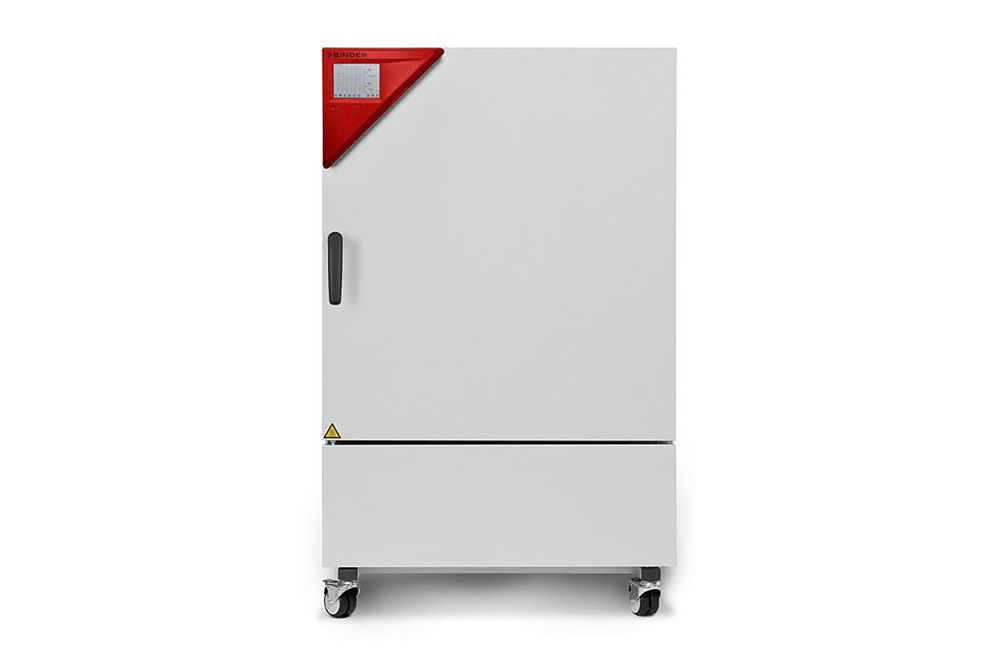

Constant Climate Chambers
Humidity test chambers with ICH-compliant light source

Moisture content affects the processability, shelf-life, usability and quality of a product. Accurate moisture content determination therefore plays a key role in ensuring quality in pharmaceuticals.
Application
- USP <731> Loss on Drying
- USP <921> Water Determination

Drying and Heating Chambers
Outstanding temperature accuracy, homogeneous heat distribution, residue-free drying

Metrohm NIRS XDS MasterLab Analyzer
Rapid, nondestructive analyses of tablets, capsules and other solid-state dosage forms

Polarimetry is used in pharmaceutical industries for purity control and determination of concentration of substances. Testing is performed according to the requirements of Pharmacopeias by measurement of both specific and optical rotation.
Application
- USP <781> Optical Rotation
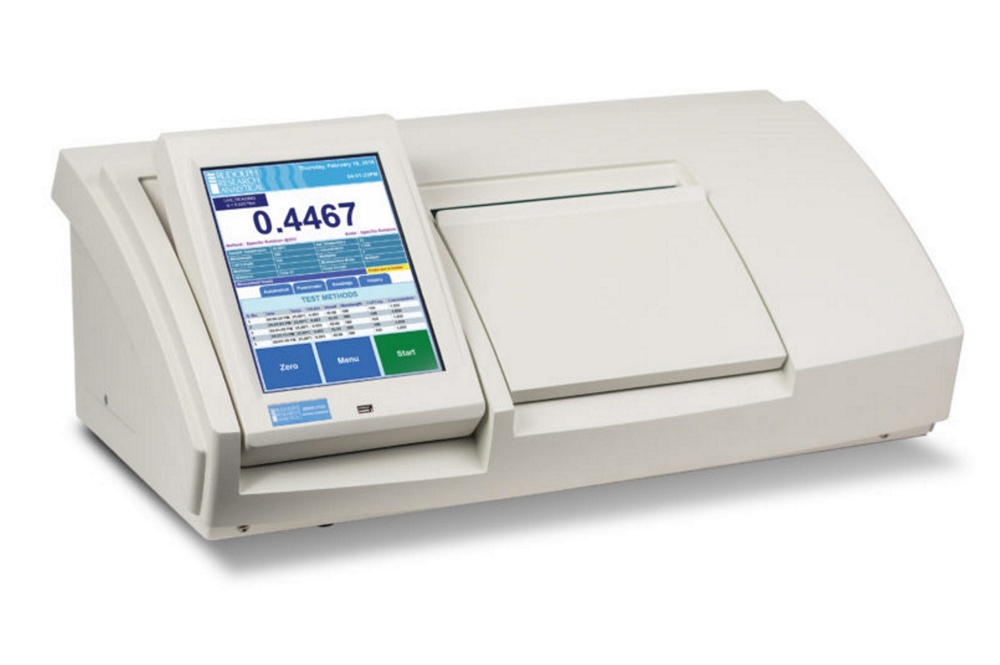

Rudolph Research Analytical Polarimeters
Polarimeters from Rudolph Research for chemical, sugar, pharmaceutical, cosmetics, essential oils, education, and university laboratories
