Inks, Paints and Coatings

Inks, Paints and Coatings
Inks, paints and coatings are generally used for depositing on an object to provide decoration, protection, corrosive prevention and other functions. As these products comprise a variety of components, the production process can be complicated.
The manufacturing of these products is faced with several challenges including raw material quality instabilities and environmental regulations compliance. Other challenges include particulate agglomeration, flowability, undesired viscosity and contamination.
For manufacturers and formulators, you need to have a strong understanding of chemical expertise, process technology and application knowledge. At DKSH, we have the experience, knowledge and a range of advanced scientific products to help you get the job done efficiently, cost-effectively and safely.
Measurement Types

Particle Size Distribution
Particle size analysis in the range 0.01-3500 microns. For nanoparticle analysis see dedicated section.

Morphology
Morphological analysis of particles in the range 0.5-10000 microns (size, shape and transparency of particles). Integrated Raman chemical analysis with MDRS (Morphologically Directed Raman Spectroscopy).
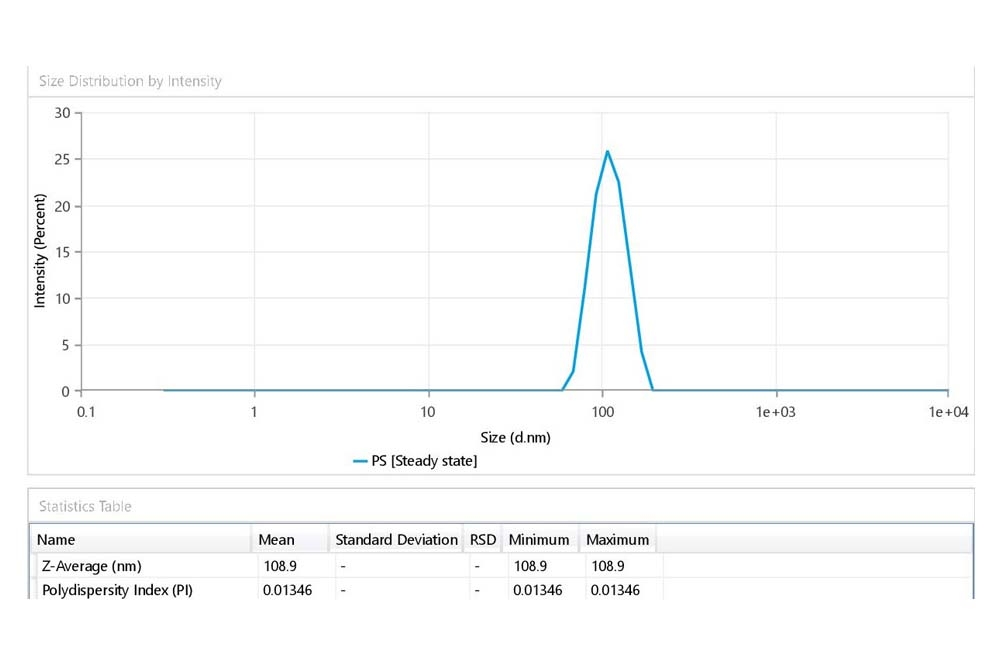
Nanoparticle Characterization
Size, concentration and zeta potential anlysis of nano-systems using light scattering techniques such as DLS, ELS and NTA techniques.
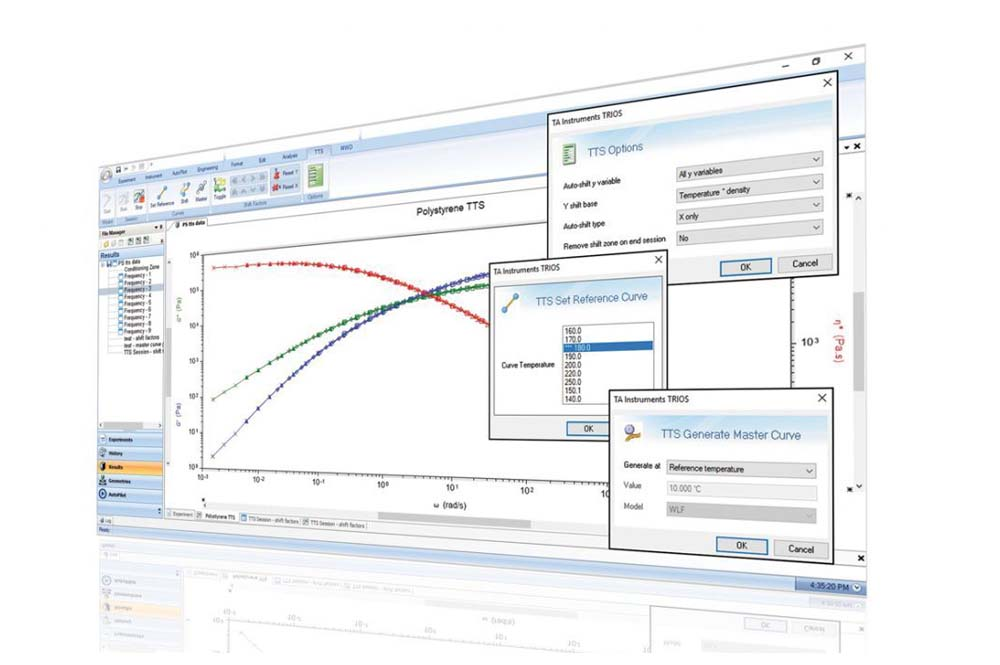
Rheology, Viscosity and Powder Flowability
Viscosity measurement and visco-elastic properties characterization of liquid dispersions, complex fluids and semi-solid materials.
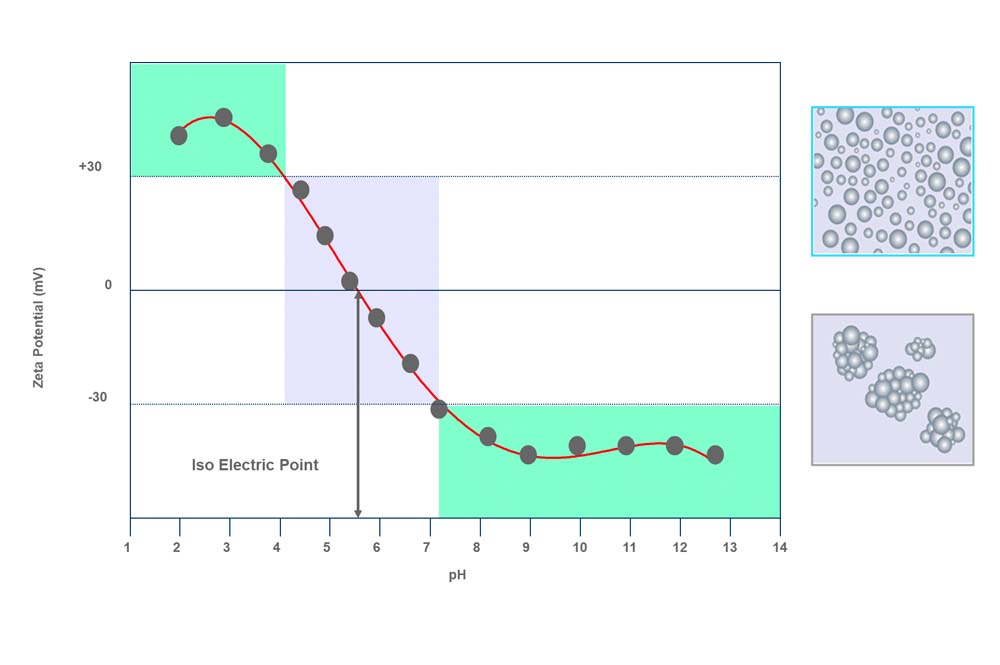
Stability Analysis
Rapid and objective quantification of concentrated dispersion real stability using Multiple Light Scattering.

High Pressure Homogenizing
High pressure homogenizing technique to produce stable nanoemulsions, reduce particle size or molecular weight of polysaccharides, nanoencapsulation, de-agglomeration, etc.
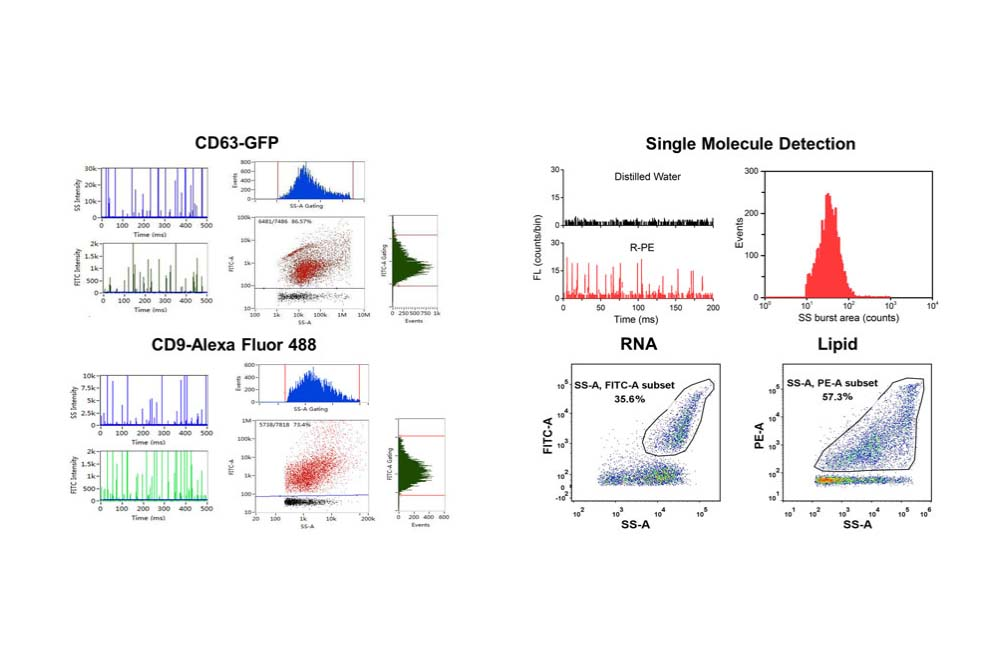
Exosomes and EVs Characterization
Multiparametric characterization of exosomes and EVs including Sizing, Concentration per size range, Count, Phenotyping, Cargo, Integrity, Purity, etc.
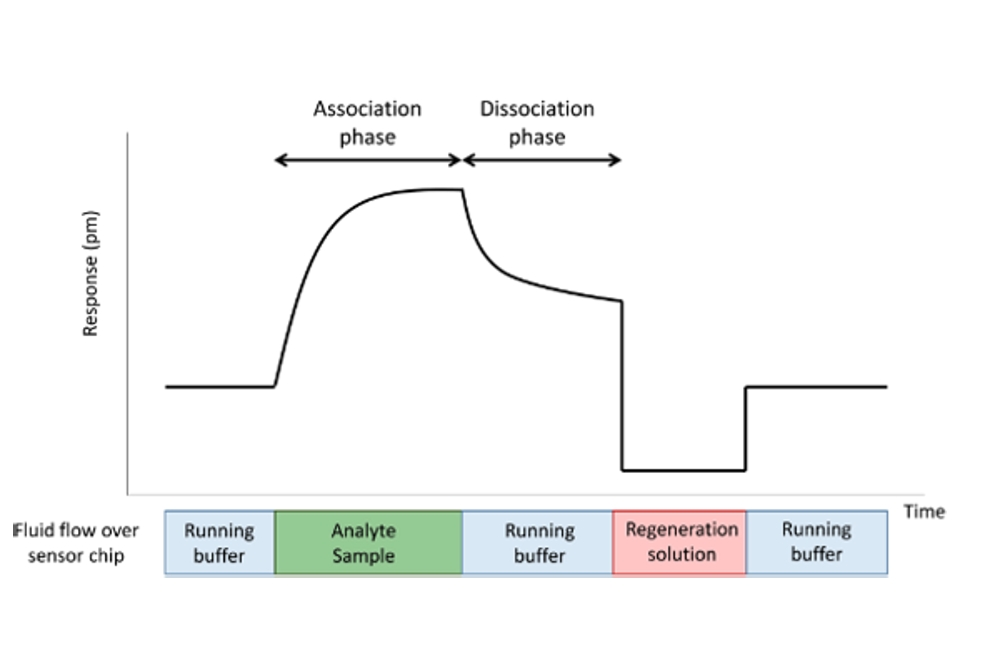
Biomolecular Interactions
Biomolecular interactions of proteins, antibodies, nucleic acids, lipids and other biomolecules using ITC Microcalorimetry or BioLayer Interferometry BLI techniques.
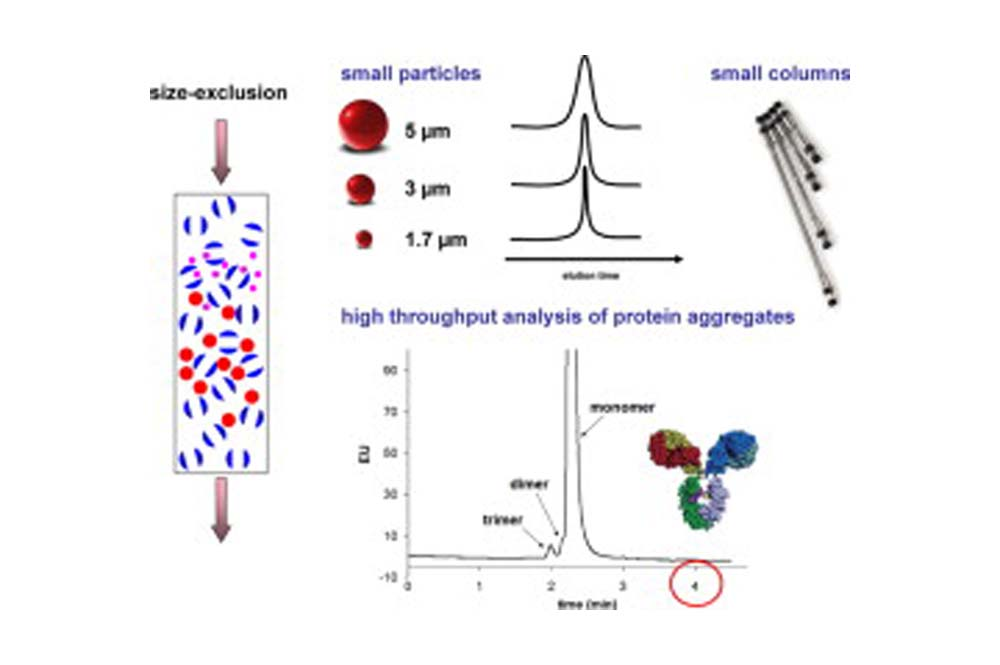
Protein Aggregate Analysis
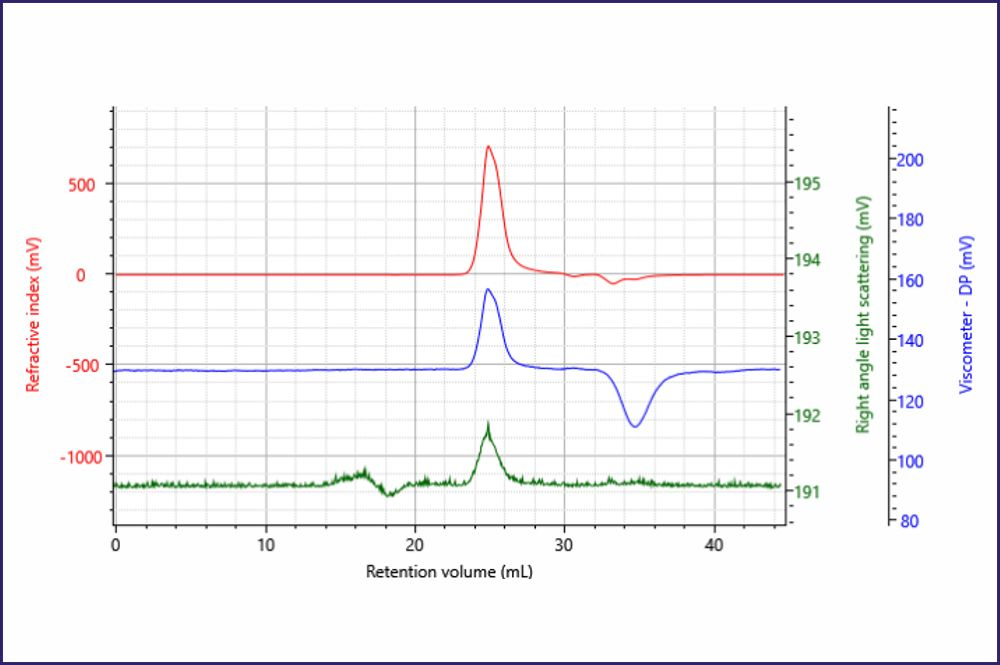
SEC is the standard method for protein aggregate analysis. The choice of pore size is related to the size of the molecule to be separated.
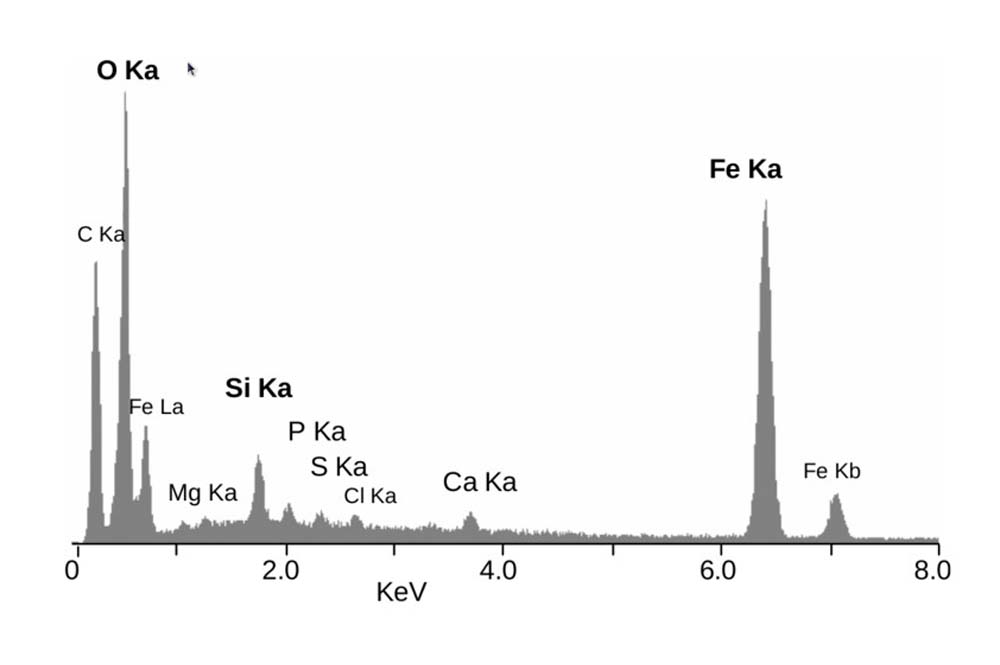
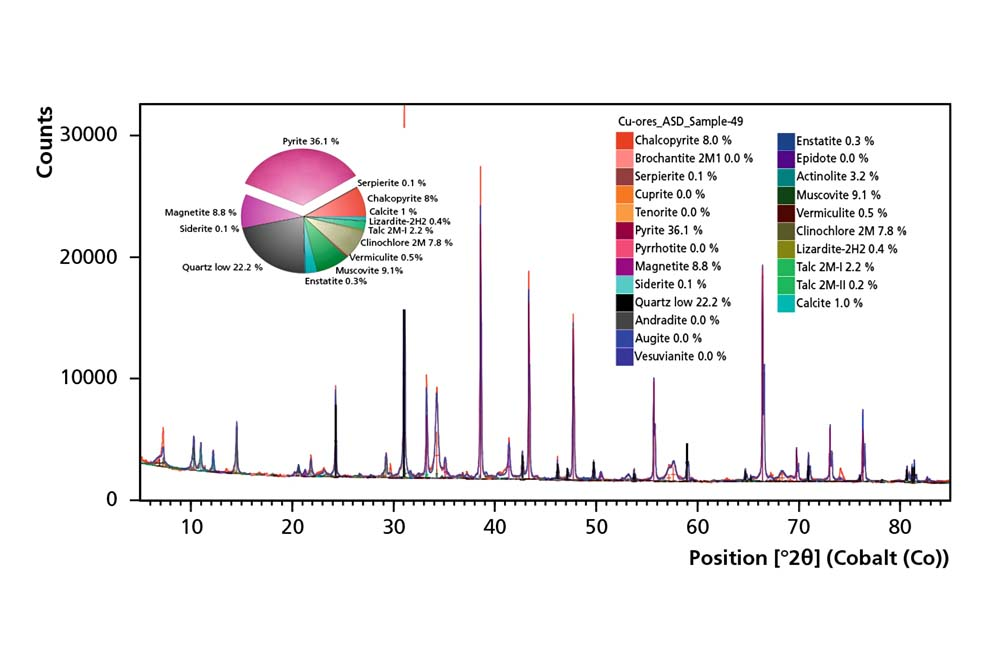
Elemental Analysis
XRF provides both qualitative and quantitative information on a wide variety of sample types. It can quantify elements from beryllium (Be) up to americium (Am) in concentrations from 100% down to sub-ppm level.
Subscribe now
Stay updated with the latest news and offers